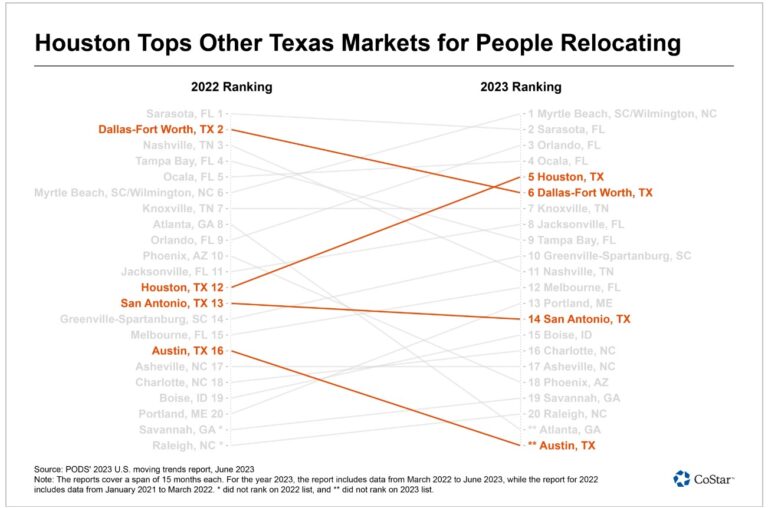
As the global economy strives to recover from the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, central banks face a daunting task in their efforts to combat rising inflation. The fight against inflation has reached a critical stage, with the last mile presenting the greatest challenges.
Inflation, the increase in general prices over time, has become a major concern for policymakers worldwide. Central banks have implemented various measures to mitigate the economic fallout caused by the pandemic, such as slashing interest rates and injecting liquidity into financial markets. However, these accommodative policies, while necessary to support economic recovery, have also contributed to the surge in inflationary pressures.
The Wall Street Journal’s analysis indicates that the most challenging phase lies ahead in the battle against inflation. Inflationary pressures have already begun to manifest across different sectors of the economy, impacting consumer prices, wages, and supply chains. This surge in prices has prompted central banks to reassess their strategies and consider measures to rein in inflation.
The Federal Reserve, for instance, is contemplating reducing its asset purchases and gradually increasing interest rates to curb inflationary pressures. The European Central Bank and the Bank of England are also reassessing their monetary policies to address rising inflation. These central banks face a delicate balancing act, as prematurely tightening monetary policy could stifle economic growth, while delaying action may exacerbate inflationary pressures.
Moreover, the global nature of today’s economy presents additional challenges in the fight against inflation. Disruptions in global supply chains, driven by factors such as shipping bottlenecks and raw material shortages, have contributed to price increases for goods and services. These challenges require coordinated efforts among central banks and policymakers worldwide to effectively tackle inflation.
Inflation expectations play a crucial role in the fight against rising prices. If consumers and businesses anticipate further price increases, they may alter their behavior by reducing spending or demanding higher wages, exacerbating inflationary pressures. Central banks must communicate effectively and manage inflation expectations to maintain price stability and anchor long-term inflationary trends.
The uneven impact of inflation on different groups within society poses social and political challenges. Rising prices disproportionately affect low-income individuals and households, exacerbating income inequality and potentially leading to social unrest. Policymakers must consider the distributional implications of their actions and implement measures to protect vulnerable populations from the adverse effects of inflation.
In conclusion, the battle against inflation has reached a critical stage, with the final stretch posing significant challenges for central banks and policymakers worldwide. Balancing the need to rein in rising prices without jeopardizing economic recovery requires careful calibration of monetary policy. Coordinated efforts and effective communication will be key to navigating these challenges and ensuring price stability in the long run.











































![An In-Depth Look at Jake and Gino's Coaching Program [A Review]](https://allaboutmultifamilyinvesting.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/AAM-BMP-Blog-Covers-750-×-422px-6.jpg)


![Email Marketing Tips for Multifamily Real Estate Syndicators to Raise Capital [Templates included]](https://allaboutmultifamilyinvesting.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/AAM-BMP-Blog-Covers-750-×-422px-4.jpg)




![The Richest Kids In America [Book Review]](https://allaboutmultifamilyinvesting.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/AAM-BMP-Blog-Covers-750-×-422px-84.jpg)